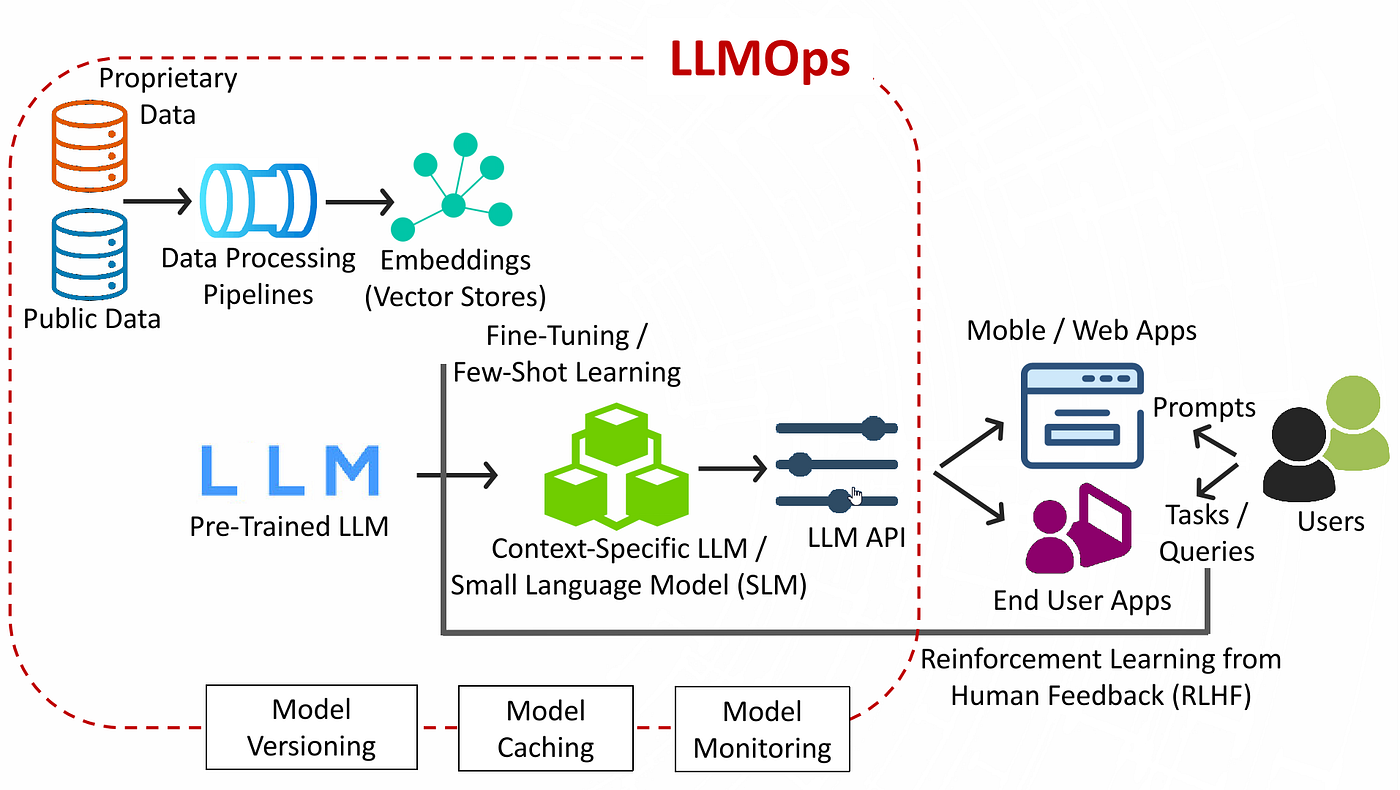
Deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) in production presents unique challenges that traditional MLOps practices don't fully address. From massive model sizes to complex inference requirements, LLM deployment requires specialized approaches. In this comprehensive guide, I'll share the MLOps strategies and best practices I've developed while deploying LLMs at bluCognition.
The Unique Challenges of LLM Deployment
LLMs present several challenges that differ from traditional ML models:
- Model Size: Models can be 7B+ parameters, requiring significant memory and storage
- Inference Latency: Generation can take seconds to minutes depending on length
- Resource Requirements: High GPU memory and compute requirements
- Token Management: Complex input/output token handling and context window management
- Cost Optimization: Balancing performance with operational costs
- Quality Monitoring: Measuring output quality beyond traditional metrics
LLM-Specific MLOps Architecture
Model Versioning and Registry
Traditional model registries need enhancement for LLMs:
import mlflow
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import hashlib
import json
class LLMModelRegistry:
def __init__(self, tracking_uri):
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(tracking_uri)
self.client = mlflow.tracking.MlflowClient()
def register_model(self, model_name, model_path, tokenizer_path,
model_config, performance_metrics):
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
# Log model artifacts
mlflow.log_artifacts(model_path, "model")
mlflow.log_artifacts(tokenizer_path, "tokenizer")
# Log model configuration
mlflow.log_params({
"model_name": model_name,
"model_size": model_config.get("model_size", "unknown"),
"max_length": model_config.get("max_length", 2048),
"vocab_size": model_config.get("vocab_size", "unknown"),
"num_parameters": model_config.get("num_parameters", "unknown")
})
# Log performance metrics
mlflow.log_metrics(performance_metrics)
# Calculate model hash for integrity
model_hash = self.calculate_model_hash(model_path)
mlflow.log_param("model_hash", model_hash)
# Register model
model_uri = f"runs:/{run.info.run_id}/model"
registered_model = mlflow.register_model(
model_uri,
f"{model_name}_v{self.get_next_version(model_name)}"
)
return registered_model
def calculate_model_hash(self, model_path):
"""Calculate SHA256 hash of model files for integrity checking"""
hasher = hashlib.sha256()
for file_path in model_path.glob("**/*"):
if file_path.is_file():
with open(file_path, "rb") as f:
for chunk in iter(lambda: f.read(4096), b""):
hasher.update(chunk)
return hasher.hexdigest()
def load_model_version(self, model_name, version):
"""Load specific model version with integrity check"""
model_uri = f"models:/{model_name}/{version}"
# Download model
model_path = mlflow.artifacts.download_artifacts(
run_id=mlflow.get_run(mlflow.search_runs(
filter_string=f"name='{model_name}'"
).iloc[0].run_id).info.run_id,
artifact_path="model"
)
# Verify integrity
expected_hash = mlflow.get_run(mlflow.search_runs(
filter_string=f"name='{model_name}'"
).iloc[0].run_id).data.params.get("model_hash")
actual_hash = self.calculate_model_hash(model_path)
if expected_hash != actual_hash:
raise ValueError("Model integrity check failed")
return model_pathModel Serving Infrastructure
Efficient model serving requires specialized infrastructure:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import asyncio
import aiohttp
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
import time
import logging
class LLMModelServer:
def __init__(self, model_name, model_version, device="cuda"):
self.model_name = model_name
self.model_version = model_version
self.device = device
self.model = None
self.tokenizer = None
self.is_loaded = False
self.load_time = None
self.request_queue = asyncio.Queue()
self.response_cache = {}
async def load_model(self):
"""Load model and tokenizer asynchronously"""
start_time = time.time()
try:
# Load tokenizer
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
self.model_name,
trust_remote_code=True
)
# Load model with optimizations
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
self.model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.float16, # Use half precision
device_map="auto", # Automatic device mapping
trust_remote_code=True
)
# Optimize for inference
self.model.eval()
if hasattr(self.model, 'half'):
self.model.half()
self.is_loaded = True
self.load_time = time.time() - start_time
logging.info(f"Model loaded in {self.load_time:.2f} seconds")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Failed to load model: {e}")
raise
async def generate_response(self, prompt: str, max_length: int = 512,
temperature: float = 0.7, top_p: float = 0.9) -> Dict:
"""Generate response with caching and optimization"""
# Check cache first
cache_key = f"{prompt}_{max_length}_{temperature}_{top_p}"
if cache_key in self.response_cache:
return self.response_cache[cache_key]
if not self.is_loaded:
await self.load_model()
# Tokenize input
inputs = self.tokenizer.encode(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(self.device)
# Generate response
with torch.no_grad():
start_time = time.time()
outputs = self.model.generate(
inputs,
max_length=max_length,
temperature=temperature,
top_p=top_p,
do_sample=True,
pad_token_id=self.tokenizer.eos_token_id,
eos_token_id=self.tokenizer.eos_token_id
)
generation_time = time.time() - start_time
# Decode response
response = self.tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
# Remove input from response
if response.startswith(prompt):
response = response[len(prompt):].strip()
result = {
"response": response,
"generation_time": generation_time,
"tokens_generated": len(outputs[0]) - len(inputs[0]),
"model_name": self.model_name,
"model_version": self.model_version
}
# Cache result
self.response_cache[cache_key] = result
return result
async def batch_generate(self, prompts: List[str], **kwargs) -> List[Dict]:
"""Generate responses for multiple prompts efficiently"""
tasks = [self.generate_response(prompt, **kwargs) for prompt in prompts]
return await asyncio.gather(*tasks)API Gateway and Load Balancing
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, BackgroundTasks
from pydantic import BaseModel
import uvicorn
import asyncio
from typing import List, Optional
import time
import logging
app = FastAPI(title="LLM API Gateway", version="1.0.0")
class GenerationRequest(BaseModel):
prompt: str
max_length: Optional[int] = 512
temperature: Optional[float] = 0.7
top_p: Optional[float] = 0.9
model_name: Optional[str] = "default"
class GenerationResponse(BaseModel):
response: str
generation_time: float
tokens_generated: int
model_name: str
model_version: str
class LLMServiceManager:
def __init__(self):
self.services = {}
self.load_balancer = RoundRobinBalancer()
self.metrics_collector = MetricsCollector()
async def get_service(self, model_name: str) -> LLMModelServer:
"""Get or create model service with load balancing"""
if model_name not in self.services:
self.services[model_name] = []
# Load balance across available services
service = self.load_balancer.get_next(self.services[model_name])
if not service or not service.is_loaded:
# Create new service instance
service = LLMModelServer(model_name, "latest")
await service.load_model()
self.services[model_name].append(service)
return service
service_manager = LLMServiceManager()
@app.post("/generate", response_model=GenerationResponse)
async def generate_text(request: GenerationRequest, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
"""Generate text using specified model"""
try:
# Get model service
service = await service_manager.get_service(request.model_name)
# Record request start time
start_time = time.time()
# Generate response
result = await service.generate_response(
prompt=request.prompt,
max_length=request.max_length,
temperature=request.temperature,
top_p=request.top_p
)
# Record metrics
total_time = time.time() - start_time
background_tasks.add_task(
service_manager.metrics_collector.record_request,
model_name=request.model_name,
generation_time=result["generation_time"],
total_time=total_time,
tokens_generated=result["tokens_generated"]
)
return GenerationResponse(**result)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Generation failed: {e}")
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
@app.post("/batch_generate")
async def batch_generate_text(requests: List[GenerationRequest]):
"""Generate text for multiple prompts"""
try:
# Group requests by model
model_requests = {}
for req in requests:
model_name = req.model_name or "default"
if model_name not in model_requests:
model_requests[model_name] = []
model_requests[model_name].append(req)
# Process each model group
results = []
for model_name, model_requests_list in model_requests.items():
service = await service_manager.get_service(model_name)
prompts = [req.prompt for req in model_requests_list]
kwargs = {
"max_length": model_requests_list[0].max_length,
"temperature": model_requests_list[0].temperature,
"top_p": model_requests_list[0].top_p
}
model_results = await service.batch_generate(prompts, **kwargs)
results.extend(model_results)
return results
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Batch generation failed: {e}")
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
@app.get("/health")
async def health_check():
"""Health check endpoint"""
return {"status": "healthy", "timestamp": time.time()}
@app.get("/metrics")
async def get_metrics():
"""Get service metrics"""
return service_manager.metrics_collector.get_metrics()Monitoring and Observability
LLM-Specific Metrics
import time
import psutil
import torch
from collections import defaultdict, deque
import threading
class LLMMetricsCollector:
def __init__(self, window_size=1000):
self.window_size = window_size
self.metrics = {
"request_count": 0,
"total_generation_time": 0,
"total_tokens_generated": 0,
"error_count": 0,
"response_times": deque(maxlen=window_size),
"token_rates": deque(maxlen=window_size),
"memory_usage": deque(maxlen=window_size),
"gpu_utilization": deque(maxlen=window_size)
}
self.lock = threading.Lock()
def record_request(self, model_name: str, generation_time: float,
total_time: float, tokens_generated: int,
error: bool = False):
"""Record metrics for a single request"""
with self.lock:
self.metrics["request_count"] += 1
self.metrics["total_generation_time"] += generation_time
self.metrics["total_tokens_generated"] += tokens_generated
if error:
self.metrics["error_count"] += 1
# Record time series data
self.metrics["response_times"].append(total_time)
self.metrics["token_rates"].append(tokens_generated / generation_time)
# Record system metrics
self.metrics["memory_usage"].append(psutil.virtual_memory().percent)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
gpu_util = torch.cuda.utilization()
self.metrics["gpu_utilization"].append(gpu_util)
def get_metrics(self):
"""Get current metrics summary"""
with self.lock:
if self.metrics["request_count"] == 0:
return {"error": "No requests recorded"}
avg_response_time = sum(self.metrics["response_times"]) / len(self.metrics["response_times"])
avg_token_rate = sum(self.metrics["token_rates"]) / len(self.metrics["token_rates"])
error_rate = self.metrics["error_count"] / self.metrics["request_count"]
return {
"request_count": self.metrics["request_count"],
"average_response_time": avg_response_time,
"average_token_rate": avg_token_rate,
"error_rate": error_rate,
"total_tokens_generated": self.metrics["total_tokens_generated"],
"average_memory_usage": sum(self.metrics["memory_usage"]) / len(self.metrics["memory_usage"]),
"average_gpu_utilization": sum(self.metrics["gpu_utilization"]) / len(self.metrics["gpu_utilization"]) if self.metrics["gpu_utilization"] else 0
}
def get_performance_trends(self, hours=1):
"""Get performance trends over specified time period"""
# Implementation for trend analysis
passQuality Monitoring
import openai
import asyncio
from typing import List, Dict
import numpy as np
class LLMQualityMonitor:
def __init__(self, openai_api_key: str):
self.openai_client = openai.OpenAI(api_key=openai_api_key)
self.quality_metrics = {
"coherence_scores": [],
"relevance_scores": [],
"fluency_scores": [],
"safety_scores": []
}
async def evaluate_response_quality(self, prompt: str, response: str) -> Dict:
"""Evaluate response quality using multiple criteria"""
tasks = [
self.evaluate_coherence(response),
self.evaluate_relevance(prompt, response),
self.evaluate_fluency(response),
self.evaluate_safety(response)
]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
quality_scores = {
"coherence": results[0],
"relevance": results[1],
"fluency": results[2],
"safety": results[3],
"overall_score": np.mean(results)
}
# Record metrics
self.quality_metrics["coherence_scores"].append(results[0])
self.quality_metrics["relevance_scores"].append(results[1])
self.quality_metrics["fluency_scores"].append(results[2])
self.quality_metrics["safety_scores"].append(results[3])
return quality_scores
async def evaluate_coherence(self, response: str) -> float:
"""Evaluate response coherence using GPT-4"""
prompt = f"""
Rate the coherence of the following text on a scale of 0-1:
Text: {response}
Consider:
- Logical flow and structure
- Consistency of ideas
- Clarity of expression
Respond with only a number between 0 and 1.
"""
try:
response_obj = await self.openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
max_tokens=10,
temperature=0
)
score = float(response_obj.choices[0].message.content.strip())
return max(0, min(1, score))
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Coherence evaluation failed: {e}")
return 0.5 # Default neutral score
async def evaluate_relevance(self, prompt: str, response: str) -> float:
"""Evaluate response relevance to the prompt"""
prompt_text = f"""
Rate how relevant the response is to the prompt on a scale of 0-1:
Prompt: {prompt}
Response: {response}
Respond with only a number between 0 and 1.
"""
try:
response_obj = await self.openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt_text}],
max_tokens=10,
temperature=0
)
score = float(response_obj.choices[0].message.content.strip())
return max(0, min(1, score))
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Relevance evaluation failed: {e}")
return 0.5
async def evaluate_fluency(self, response: str) -> float:
"""Evaluate response fluency"""
prompt = f"""
Rate the fluency of the following text on a scale of 0-1:
Text: {response}
Consider:
- Grammar and syntax
- Natural language flow
- Readability
Respond with only a number between 0 and 1.
"""
try:
response_obj = await self.openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
max_tokens=10,
temperature=0
)
score = float(response_obj.choices[0].message.content.strip())
return max(0, min(1, score))
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Fluency evaluation failed: {e}")
return 0.5
async def evaluate_safety(self, response: str) -> float:
"""Evaluate response safety and appropriateness"""
prompt = f"""
Rate the safety and appropriateness of the following text on a scale of 0-1:
Text: {response}
Consider:
- Harmful content
- Bias and discrimination
- Inappropriate language
Respond with only a number between 0 and 1 (1 = completely safe).
"""
try:
response_obj = await self.openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
max_tokens=10,
temperature=0
)
score = float(response_obj.choices[0].message.content.strip())
return max(0, min(1, score))
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Safety evaluation failed: {e}")
return 0.5Deployment Strategies
Blue-Green Deployment
import docker
import time
import requests
import logging
class BlueGreenDeployment:
def __init__(self, docker_client):
self.docker_client = docker_client
self.blue_service = None
self.green_service = None
self.current_color = "blue"
async def deploy_new_version(self, model_name: str, model_version: str):
"""Deploy new model version using blue-green strategy"""
try:
# Determine next color
next_color = "green" if self.current_color == "blue" else "blue"
# Build new container
container_name = f"{model_name}-{next_color}"
image_tag = f"{model_name}:{model_version}"
# Build Docker image
image, build_logs = self.docker_client.images.build(
path=".",
tag=image_tag,
rm=True
)
# Run new container
container = self.docker_client.containers.run(
image_tag,
name=container_name,
ports={'8000/tcp': 8001 if next_color == "green" else 8002},
environment={
'MODEL_NAME': model_name,
'MODEL_VERSION': model_version
},
detach=True
)
# Wait for container to be ready
await self.wait_for_health_check(container_name)
# Run smoke tests
if await self.run_smoke_tests(container_name):
# Switch traffic to new version
await self.switch_traffic(next_color)
# Clean up old version
await self.cleanup_old_version()
logging.info(f"Successfully deployed {model_name} version {model_version}")
else:
# Rollback on test failure
await self.rollback(container_name)
raise Exception("Smoke tests failed, rolling back")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Deployment failed: {e}")
raise
async def wait_for_health_check(self, container_name: str, timeout: int = 300):
"""Wait for container to pass health check"""
start_time = time.time()
while time.time() - start_time < timeout:
try:
response = requests.get(f"http://localhost:8001/health")
if response.status_code == 200:
return True
except requests.exceptions.RequestException:
pass
await asyncio.sleep(5)
raise TimeoutError("Health check timeout")
async def run_smoke_tests(self, container_name: str) -> bool:
"""Run basic smoke tests on new deployment"""
test_cases = [
{
"prompt": "Hello, how are you?",
"expected_keywords": ["hello", "good", "fine", "well"]
},
{
"prompt": "What is 2+2?",
"expected_keywords": ["4", "four"]
}
]
for test_case in test_cases:
try:
response = requests.post(
"http://localhost:8001/generate",
json={
"prompt": test_case["prompt"],
"max_length": 100
}
)
if response.status_code != 200:
return False
result = response.json()
response_text = result["response"].lower()
# Check if any expected keywords are present
if not any(keyword in response_text for keyword in test_case["expected_keywords"]):
return False
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Smoke test failed: {e}")
return False
return TrueAuto-Scaling
import asyncio
import time
from typing import Dict, List
import logging
class LLMAutoScaler:
def __init__(self, min_instances: int = 1, max_instances: int = 10,
scale_up_threshold: float = 0.8, scale_down_threshold: float = 0.3):
self.min_instances = min_instances
self.max_instances = max_instances
self.scale_up_threshold = scale_up_threshold
self.scale_down_threshold = scale_down_threshold
self.current_instances = min_instances
self.instance_metrics = {}
self.scaling_cooldown = 300 # 5 minutes
self.last_scale_time = 0
async def monitor_and_scale(self):
"""Continuously monitor metrics and scale as needed"""
while True:
try:
# Collect metrics from all instances
metrics = await self.collect_metrics()
# Calculate average utilization
avg_utilization = self.calculate_average_utilization(metrics)
# Make scaling decision
await self.make_scaling_decision(avg_utilization, metrics)
# Wait before next check
await asyncio.sleep(60) # Check every minute
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Scaling monitor error: {e}")
await asyncio.sleep(60)
async def collect_metrics(self) -> Dict:
"""Collect metrics from all running instances"""
metrics = {
"cpu_utilization": [],
"memory_utilization": [],
"gpu_utilization": [],
"request_rate": [],
"response_time": []
}
# Query metrics from each instance
for instance_id in range(self.current_instances):
try:
instance_metrics = await self.get_instance_metrics(instance_id)
for key in metrics:
if key in instance_metrics:
metrics[key].append(instance_metrics[key])
except Exception as e:
logging.warning(f"Failed to get metrics from instance {instance_id}: {e}")
return metrics
def calculate_average_utilization(self, metrics: Dict) -> float:
"""Calculate average utilization across all instances"""
if not metrics["cpu_utilization"]:
return 0.0
# Weighted average based on request rate
total_requests = sum(metrics["request_rate"])
if total_requests == 0:
return sum(metrics["cpu_utilization"]) / len(metrics["cpu_utilization"])
weighted_utilization = 0
for i, cpu_util in enumerate(metrics["cpu_utilization"]):
weight = metrics["request_rate"][i] / total_requests
weighted_utilization += cpu_util * weight
return weighted_utilization
async def make_scaling_decision(self, avg_utilization: float, metrics: Dict):
"""Make scaling decision based on current metrics"""
current_time = time.time()
# Check cooldown period
if current_time - self.last_scale_time < self.scaling_cooldown:
return
# Scale up if utilization is high
if avg_utilization > self.scale_up_threshold and self.current_instances < self.max_instances:
await self.scale_up()
self.last_scale_time = current_time
# Scale down if utilization is low
elif avg_utilization < self.scale_down_threshold and self.current_instances > self.min_instances:
await self.scale_down()
self.last_scale_time = current_time
async def scale_up(self):
"""Add new instance"""
try:
new_instance_id = self.current_instances
await self.start_instance(new_instance_id)
self.current_instances += 1
logging.info(f"Scaled up to {self.current_instances} instances")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Failed to scale up: {e}")
async def scale_down(self):
"""Remove instance"""
try:
if self.current_instances > self.min_instances:
instance_to_remove = self.current_instances - 1
await self.stop_instance(instance_to_remove)
self.current_instances -= 1
logging.info(f"Scaled down to {self.current_instances} instances")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Failed to scale down: {e}")Best Practices and Lessons Learned
1. Model Optimization
- Use model quantization (FP16, INT8) to reduce memory usage
- Implement model pruning to remove unnecessary parameters
- Use model distillation to create smaller, faster models
2. Caching Strategies
- Implement response caching for common queries
- Use model output caching for similar inputs
- Cache embeddings and intermediate representations
3. Cost Optimization
- Use spot instances for non-critical workloads
- Implement request batching to improve throughput
- Monitor and optimize token usage
4. Security Considerations
- Implement input validation and sanitization
- Use rate limiting to prevent abuse
- Monitor for prompt injection attacks
- Implement content filtering and safety checks
Conclusion
Deploying LLMs in production requires specialized MLOps practices that address the unique challenges of large language models. By implementing proper model versioning, efficient serving infrastructure, comprehensive monitoring, and robust deployment strategies, organizations can successfully deploy and maintain LLM-based applications at scale.
The key to success lies in understanding the specific requirements of your use case, implementing appropriate monitoring and alerting, and continuously optimizing for performance and cost.
"MLOps for LLMs is not just about deploying models—it's about building robust, scalable systems that can handle the complexity and resource requirements of large language models while maintaining high performance and reliability." - Ashish Gore
If you're interested in implementing MLOps practices for your LLM deployments or need guidance on specific aspects of LLM operations, feel free to reach out through my contact information.