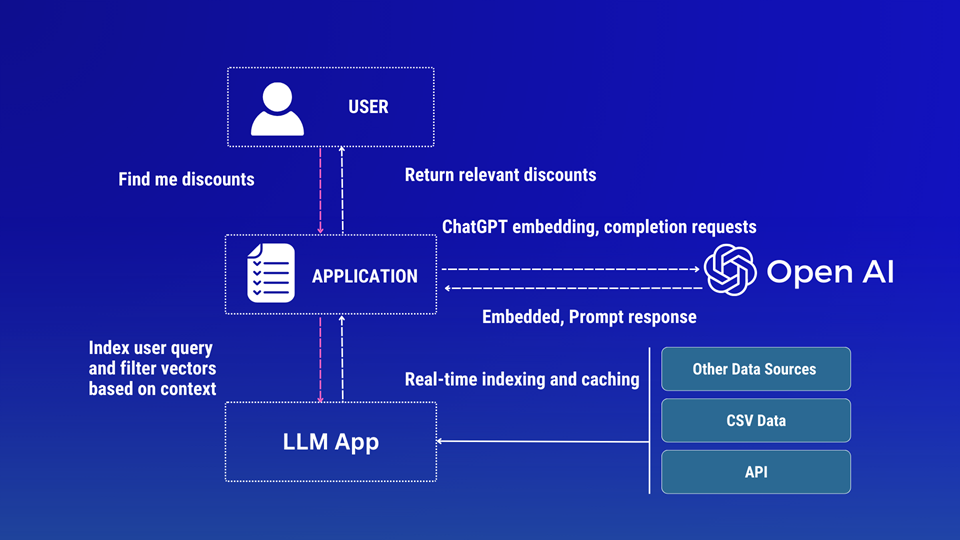
One of the most powerful features introduced by OpenAI is the ability to extend ChatGPT with plugins. These plugins allow the model to access external data sources, perform real-time actions, and integrate seamlessly with third-party APIs.
What Are ChatGPT Plugins?
Plugins are essentially lightweight APIs that the model can call when needed. Instead of relying only on its training data, ChatGPT can connect to live systems to fetch information, perform calculations, or trigger workflows.
Setting Up Your First Plugin
To create a ChatGPT plugin, you’ll need three main components:
- API: The backend service (e.g., Flask or FastAPI).
- Manifest File: JSON file that describes the plugin.
- OpenAPI Spec: Defines the endpoints and request/response structure.
1. Example Plugin with Flask
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/weather", methods=["GET"])
def get_weather():
city = request.args.get("city", "Unknown")
return jsonify({
"city": city,
"temperature": "24°C",
"condition": "Sunny"
})
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(port=5000)2. Manifest File (ai-plugin.json)
{
"schema_version": "v1",
"name_for_human": "Weather Plugin",
"name_for_model": "weather",
"description_for_model": "Get current weather information for a city.",
"auth": {"type": "none"},
"api": {"type": "openapi", "url": "http://localhost:5000/openapi.json"},
"logo_url": "http://localhost:5000/logo.png",
"contact_email": "support@example.com",
"legal_info_url": "http://example.com/legal"
}3. OpenAPI Spec
{
"openapi": "3.0.1",
"info": {"title": "Weather API", "version": "1.0.0"},
"paths": {
"/weather": {
"get": {
"summary": "Get current weather by city",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "city",
"in": "query",
"required": true,
"schema": {"type": "string"}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Successful response",
"content": {"application/json": {"example": {"city": "Paris", "temperature": "22°C"}}}
}
}
}
}
}
}Testing the Plugin
Once you have your Flask server, manifest, and OpenAPI spec ready, you can register the plugin in ChatGPT. The model will then know when to call your plugin.
Real-World Examples
- Finance: Query stock prices and generate trading insights.
- Productivity: Connect with calendars, to-do lists, or CRM tools.
- Travel: Fetch live flight details and booking information.
- Enterprise: Integrate with internal knowledge bases or databases.
Best Practices
- Design endpoints with clear and concise responses for the model to interpret easily.
- Include strong validation and error handling in your API.
- Use authentication (OAuth, API keys) for sensitive data sources.
- Keep responses lightweight to reduce token usage.
Conclusion
ChatGPT plugins extend the model’s abilities beyond static knowledge, enabling it to interact with the real world. By building simple APIs and registering them as plugins, developers can create powerful AI-driven applications tailored to specific domains.
"Plugins transform LLMs from passive text generators into active problem-solvers with access to live data and actions." - Ashish Gore
If you’d like to build or experiment with custom ChatGPT plugins, feel free to reach out through my contact information.